This week in triple science we have learnt about polymers and the structure of DNA. On Monday we learnt about polyesters. We also learnt about condensation reactions. Condensation reactions is a reaction in which two small molecules react form a larger molecule, with the elimination of water. To make a polyester by condensation you will need to draw out separately your diacid (which is a dicarboxylic acid) and your diol (which is your alcohol). You would then take away two of the H’s s and one O you take these away because they are lost to make water. After you have taken the water away you join the two together to make a polyester but you have to put a big bracket around each of then ends and draw lines through the bracket this is to show that the polyester and then be bonded on to other polyesters then you have to put a lowercase “n”. An example of how you lay it out is shown below. An example of a condensation reaction is of propanediol and butanedioic acid.

On Thursday which was our next triple science lesson we learnt about the structure of DNA. We learnt that DNA is made up of two strands and that it is made up of monomers known as nucleotide. The shape of a DNA strand is a double helix. We also learnt that there are four different nucleotides these are known as Adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine. Adenine pairs with thymine. guanine pairs with cytosine. For example, if strand 1 was ATGGCATAGGCAT then strand 2 would be TACCGTATCCGTA. We also learnt about the structure of the DNA strands. This is a DNA strand example and what each piece breaks into
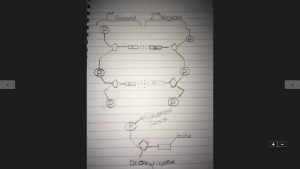
We also learnt that each 3 bases = triplet. Each triplet codes for a different amino acid. Each amino acid makes a different protein. Genes code for protein, proteins are made up of amino acids. Genetic codes are degenerate as more than 1 triplet can code for an amino acid. On Friday we did some revision on different topic in biology and created flash cards with the question and answers on them. Some of the questions were:
List the different organelles in a plant and their functions?
Nucleus- where DNA is found and controls the cell
Vacuole- stores water
Ribosomes- makes protein
Cell wall-supports the shape of the cell
Cell membrane- allows substances In and out of the cell
Chloroplast- where photosynthesis happens
Mitochondria- releases energy. site of aerobic respiration
Cytoplasm-where chemical reactions occur
Another question was:
What is active transport?
Active transport is where substances need to be absorbed against a concentration gradient from a low concentration to a high concentration. Active transport requires energy and a protein carrier. Happens across a partially-permeable membrane.